Communicating Results
Roughly two-thirds of Wisconsinites rely on groundwater for their drinking water.
Understand what makes a well vulnerable, susceptible contaminants, and the health risks associated with drinking water exceeding state standards. Work together with county public health departments to provide support to communities vulnerable to well contamination.

Supporting private well owners

A Guide to Buying and Managing Rural Acres
Country Acres: A Guide to Buying and Managing Rural Acres Share Extension's 1999 packet with new rural homeowners to help understand how to safely maintain rural property.

A Guide to an Educational Water Testing Program
Guide to Organizing a Community Drinking Water Testing and Educational Program - UW - Stevens Point (UWSP) Center for Watershed Science and Education's Guide to Organizing a Community Drinking Water Testing and Educational Program

Maintaining a Private Well
The Dept. of Health Services dedicates this webpage to support private well owners maintaining their wells, understanding potential impacts, and contaminants to consider monitoring for.
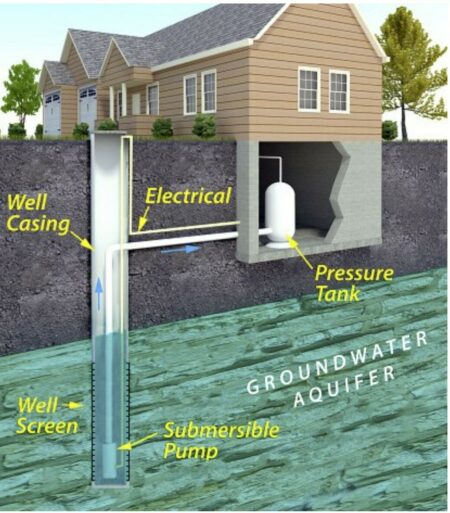
Well Construction Matters
Visit this EPA website that describes the types of wells, components of well construction, and how construction can contribute contamination vulnerability.
Learn MoreCommon contaminants associated with land use
The groundwater standards for nitrate were adopted in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement standard = 10 mg/L (as nitrate-nitrogen)*
- Preventive action limit = 2 mg/L (as nitrate-nitrogen)*
Bacteria (Escherichia coli)
The groundwater standards for Escherichia coli (E.coli) were recommended in Cycle 10 (2019). The rule to adopt these standards was approved by the Governor on February 2, 2023.
- Recommended enforcement standard = 0 CFU
- Recommended preventive action limit = 0 CFU
Bacteria (total coliform)
The groundwater standards for bacteria (total coliform) was first adopted in Cycle 1 (1985), updated in Cycle 6 (1995), and reviewed as part of Cycle 10 (2019).
- Enforcement standard = 0 CFU
- Preventive action limit = 0 CFU
The groundwater standards for atrazine were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988) and updated in Cycle 4 (1992).
- Enforcement standard = 3 µg/L*
- Preventive action limit = 0.3 µg/L*
